Harper Adams University has undertaken an extensive review of the impact of drought on crops grown in the UK and their response to different climate futures. This also includes a consolidation of insights for protected and horticultural crops. This report is available in draft and more focussed crop factsheets are in production.
Tag: agriculture
Economic value of supplemental irrigation in England and Wales StoryMap
Irrigation is an essential component of crop production to meet retailer demands for premium quality when rainfall is insufficient. Under drought conditions, irrigation can be constrained by water resources availability, with consequent impacts on yield, quality and revenue. Whilst most agriculture in Europe is rainfed, greater dependence on supplemental irrigation could become more important in humid environments due to a changing climate with greater rainfall uncertainty and higher frequency of droughts.
This interactive StoryMap explores the total financial benefit of outdoor irrigated production in England and Wales assuming no constraints in resource availability and optimal irrigation practices. The analysis suggests that the total net benefits of irrigation in a dry year are around £665 million. Map outputs highlight significant regional differences in water productivity reflecting the composition of land use and the importance of crop mix in determining economic value. A sensitivity analysis to changes in agroclimate, market conditions (crop prices) and water supply (costs) illustrates how the benefits might change under contrasting scenario. The study highlights the importance of supplemental irrigation, even in a humid climate, and the risks that future droughts and/or constraints in water resource availability might have on agricultural systems, livelihoods and the rural economy.The StoryMap is based on a paper, “Modelling and mapping the economic value of supplemental irrigation in a humid climate“.
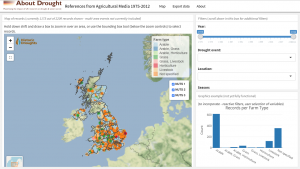
Drought impacts explorer
As part of the Historic Droughts project, researchers at Cranfield University developed an inventory of qualitative drought data related to UK agriculture based on an extensive review from two weekly farming magazines in the UK, Farmer’s Weekly and Farmers Guardian for the period 1975-2018. The resultant inventory contains over 2500 records with information on the start and end dates of the event and their location to characterise the temporal and spatial extents of the cited event, together with the text describing the driver, impact or response in relation to that event. The inventory is available to download as a csv file from the UK Data Service.
This dataset is also currently being translated in to a drought impacts explorer, which allows the user to view these records spatially and to search and save according to various criteria. If you would like to be involved in beta testing of the explorer please contact nevil.quinn@uwe.ac.uk. An early draft of the explorer is available online.
D-Risk
Recent droughts have highlighted the pressures on water allocations and the reliability of abstractions for irrigation. Farm business models need to align cropping programmes to water availability – how resilient is yours to future water shocks?
D-Risk is an intuitive and free online webtool to help farming enterprises rapidly understand their business and drought abstraction risks and thereby support robust decisions regarding future investment in irrigation infrastructure, including equipment and storage reservoirs. D-Risk uses readily accessible data on your local soils, agroclimate, crop areas, irrigation plans, licences and reservoirs to assess the risk of having:
- Insufficient headroom
- Irrigation deficit
You can then explore:
- Impact of licence changes
- Modified crop mix and irrigated areas
- Need for reservoir investment
A Water Strategy for UK Agriculture
Increasing the farming sector’s resilience to drought and water scarcity risks
Water is at the heart of farming and agri-businesses, particularly in eastern England, the east midlands, and south-east, the driest and most water-stressed areas in the UK. Without water most agri-businesses would simply not survive. Irrigated agriculture supplies the UK’s agri-food industry with substantial quantities of high-quality potatoes, fruit and vegetables. But increasing regulation, droughts and a changing climate all threaten the sustainability of this industry and the rural livelihoods it supports. While other sectors and businesses have water strategies, the agriculture sector does need. Agriculture therefore needs a water strategy to ensure that it receives a fair share of the nation’s available water resources.
To address this need researchers at Cranfield University have been working in partnership with the National Farmers Union (NFU), the UK Irrigation Association (UKIA) and other stakeholders to develop a collective vision. The strategy sets out some guiding principles and proposes actions grouped according to the following themes:
- Manage current and future demand in abstraction ‘hotspots’
- Address environmental challenges linked to over-abstraction and climate change
- Build water infrastructure to provide resilience for farming businesses
- Promote business growth and support multi-sector stakeholder engagement
Drought and Agriculture Synthesis Report

The Agricultural Synthesis report summarises the key findings that emerged from the five Drought and Water Scarcity programme projects to help the UK agriculture and horticultural sector to better understand, forecast, manage and respond to the challenges posed by droughts and water scarcity. The report summarises how drought and water scarcity affects agriculture, and the consequent impact on rainfed and irrigated agriculture. The report also considers drought forecasting and whether drought and water scarcity impacts can be reduced.
Report back from Drought & Water Scarcity Conference
Drought and Water Scarcity: addressing current and future challenges, International Conference
View presentations below
This international event was held at Pembroke College, University of Oxford over 20-21 March 2019.
Speakers from around the world gathered to present and discuss their research on drought and water scarcity. There was an impressive range of data, topics, in-depth knowledge and communication insights which demonstrated the breadth and interdisciplinary nature of research into drought and water scarcity.
Delegates heard that drought and water scarcity are expected to become more severe due to the influence of climate change and pressure on water resources from economic and demographic changes. The impacts of this affects hydrology, agriculture and farming, industry and communities. Water and the lack of water effects every aspects of society and the environment, and the lack of water has profound consequences.
You can see the full programme here.
A number of the oral and poster presenters have kindly given permission to share their work. You can access the presentations by clicking on the links below.
Presentations available to view
Amanda Fencl, University of California, Davis – “Interconnections between Research on Groundwater, Drought and Climate Change”
Anne van Loon, Birmingham University – “Drought in the Anthropocene: vulnerability & resilience”
Antonia Liguori, Loughborough University – “Learning around ‘storying water’ to build an evidence base to support better decision-making in UK drought risk management”
Ayilobeni Kikon, National Institute of Technology Karnataka – “Application of Optimized Machine Learning Technique in Drought Forecasting Using SPI”
Caroline King, CEH; co-authored with Daniel Tsegai, Programme Officer, UNCCD Secretariat – “A review of methods for drought impact and vulnerability assessment”
Cedric Laize, TBI & GeoData Institute – “Relationship between a drought-oriented streamflow index and a series of riverine biological indicators”
Christopher Nankervis, Weather Logistics Ltd – “Use of Copernicus seasonal climate forecast model data to improve the accuracy of long-term forecasts: the UK Summer Rainfall Insights project.”
Daniela Anghileri, University of Southampton – “Strengthening research capabilities for addressing water and food security challenges in sub-Saharan Africa”
Emma Cross, Environment Agency – “The 2018 heatwave; its impacts on people and the environment in Thames Area”
Elizabeth Brock, Met Office; Katherine Smart, Anglian Water – “Re-analysis of historical events using up to date extreme value techniques, to determine the return period of historical and stochastic droughts, with particular reference to ‘severe’ or 1 in 200 year return period events”
Feyera A. Hirpa, Ellen Dyer, Rob Hope, Daniel O. Olago, Simon J. Dadson, University of Oxford – “Finding sustainable water futures in the Turkwel River basin, Kenya under climate change and variability”
Fiona Lobley, Environment Agency – “2018 dry weather and its impacts; looking ahead to 2019”
Frederick Otu-Larbi, Lancaster University – “Modelling the effects of drought stress on photosynthesis and latent heat fluxes.”
Granville Davies and Miranda Foster, Yorkshire Water – “Water resources in Yorkshire, UK in 2018: drought management, perception and communication”
Harry West, University of the West of England, Bristol – “Examining spatial variations in the utility of SPI as a 3-month-ahead environmental drought indicator”
Henny van Lanen, Wageningen University & Research – “The 2018 NW European Drought: warnings from an extreme event”
Katherine Smart, Anglian Water; Elizabeth Brock, Met Office – “Re-analysis of historical events using up to date extreme value techniques, to determine the return period of historical and stochastic droughts, with particular reference to ‘severe’ or 1 in 200 year return period events”
Kerstin Stahl, Freiburg – “Customizing drought indices to improve drought impact monitoring and prediction”
Kevin Grecksch, Centre for Socio-Legal Studies, University of Oxford – “Achieving water efficiency through social norms in the public sector”
Len Shaffrey, NCAS, University of Reading – “Has climate change increased the chance of events like the 1976 North West European drought occurring?”
Lucy Barker, Centre for Ecology & Hydrology – “How severe were historic hydrological droughts in the UK? Insights from a systematic characterisation and ranking of events back to 1891”
Mark Smith, Hydro-Logic Services (International) Ltd – “Recent trends in water resources planning and management, and the rising importance of planning processes in reflecting the ‘consequences’ of relevance and interest to customers and stakeholders”
Massimiliano Pasqui, CNR – “A customizable drought monitoring and seasonal forecasting service to support different users’ needs”
Matt Fry, CEH – “The Historic Droughts Inventory: an accessible archive of past drought impact information for the UK from diverse documentary sources”
Miranda Foster and Granville Davies, Yorkshire Water – “Water resources in Yorkshire, UK in 2018: drought management, perception and communication”
Mike Morecroft, Natural England – “Drought impacts on the natural environment and lessons for climate change adaptation”
Nikos Mastrantonas, CEH – “Drought Libraries for enhanced resilience in long term water resource planning in the UK”
Paul Whitehead, University of Oxford – “Impacts of climate change on water quality affecting upland and lowland rivers, wetlands and delta systems”
Peter Anthony Cook, NCAS-Climate, Department of Meteorology, University of Reading – “Variations in the West African Monsoon from reanalysis and model results”
Peter Kettlewell, Harper Adams University – “Mitigating drought impact on crop yield by applying film-forming polymers”
Rob Wilby, Loughborough – “Challenging the mantra of wetter-winters, drier summers in the UK”
Ruth Langridge, University of California, Santa Cruz – “Groundwater management in planning for drought: experience from California, USA”
Sandra Santos, Wageningen University – “Improving institutional frameworks integrating local initiatives from communities exposed to drought and water scarcity in Ecuador”
Stephen McGuire, SEPA – “Assessing the impacts of water scarcity in Northeast Scotland through the summer of 2018.”
Wiza Mphande, Harper Adams University – “Elucidating Drought Mitigation with Antitranspirants in Spring Wheat”
Future water for food – About Drought at IRRIGEX 2019

If you are going to IRRIGEX on February 27-28, you can talk to our experts from the About Drought programme on Stand 10.
With many farmers unable to fill their reservoirs and time running out for winter fills, our leading researchers will be available at the two-day exhibition, in Peterborough, for informal conversations about the wealth of decision-supporting data About Drought has already made available.
Two of our team – Professors Ian Holman and Jerry Knox of Cranfield University also feature in the impressive programme of speakers and seminars.
In last summer’s drought some tools produced by About Drought – the £12m UK Drought & Water Scarcity Research Programme – were fast-tracked into real-time use in some sectors. Forecasts are currently indicating below average rainfall for this month and March so IRRIGEX is a timely opportunity to find out more about the tools available and how they can support your decision-making.
The theme for IRRIGEX this year is ‘Future water for food’ and it is free to attend. For full details visit www.irrigex.com. We look forward to meeting you on Stand 10.
Pollinator: Innovation to Improve Water Management
13 September 2018
Location: Easton Campus, Easton and Otley College, Norwich NR9 5DX
Event organiser: Agri-Tech East
Event type: Conference
Applications: Book online
Managing water continues to be a major challenge, ensuring the right amount in the right place at the right time. Access to water can dictate farming regimes and influence crop performance, and regulation around water management are driving investment in new solutions, both on and off-farm.
Here we’ll be considering innovative products, services and practices to help re-use, recycle and retain water in the farming ecosystem. With an emphasis on the practical aspects of water management, we’ll be looking at topics such as smart irrigation, monitoring of leaks, soil moisture retention and water storage options.
With speakers confirmed from Verdesian, Anglian Water, the Norfolk Rivers Trust and Cranfield University, book now for the chance to understand more about new solutions to manage one of our most precious and unpredictable resources.
About Drought briefing note: Which farming areas of England and Wales are most at risk from economic losses due to drought?

This briefing note looks at the effects of water scarcity and drought on crops which require supplemental irrigation, and includes some ideas on steps which may help to mitigate losses to farmers. This is the first of a series of briefs to support improved decision making in relation to droughts and water scarcity.
We are currently experiencing a heatwave in the UK and other parts of Europe – with a hosepipe ban in place in Ireland. Climatic change causes greater unreliability of rainfall in wetter countries like the UK, as well as increased frequency of droughts, leading to higher demand for irrigation to supplement rainfall. The yield and quality of crops of fruit and vegetables can be lowered by short-term drought in the UK summer – this can be avoided by using irrigation to supplement rainfall, enabling farmers to continue to provide supermarket-quality produce.